In most cases, an audit of the quality management system by a notified body is a prerequisite for manufacturers of medical devices to be allowed to market their devices in Europe.
The FDA also audits quality management systems but refers to inspections rather than audits.
Content
On this page, you will find articles on:
- The basics of audits
- The audit process
- Support with audits and the development of QM systems
1. Basics for audits
a) Definition of the term
ISO 9000:2015 defines the term audit as follows:
systematic, independent and documented process for obtaining objective evidence and evaluating it objectively to determine the extent to which the audit criteria are fulfilled.
b) The different types of audits
Depending on the focus of an audit, there are:
- System audits (e.g., inspection of the conformity of a quality management system with the requirements of a standard such as ISO 13485 or ISO 9001)
- Process audits
- Product audits
- Software audits
A distinction is also made between
c) Regulatory basis for audits
Europe
An audit by a notified body is the prerequisite for the notified body to issue a certificate (in accordance with ISO 13485 or Annex IX). This certificate in turn is the prerequisite for placing devices on the market, at least for products of higher risk classes.
Caution!
Manufacturers may only place their devices on the market on the basis of certificates from a notified body. There are other certification bodies whose ISO 13485 certificates are worthless. There are also providers who are not even accredited for ISO 13485.
USA
The FDA now also requires conformity with ISO 13485 but does not require certificates. It reviews conformity as part of FDA-inspections. However, unlike audits, inspections do not end with a certificate if they are successful.
Worldwide (“MDSAP countries”)
The International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) has launched the Medical Device Single Audit Program MDSAP: An MDSAP audit can be used to fulfill the regulatory requirements for audits and inspections of QM systems.
2. Audit procedure
a) General
ISO 19011 describes the requirements for audits (i.e., their planning, implementation and documentation) and for auditors.
Further information
Further determinations specify the duration of audits.
If an auditor certifies a “non-conformity”, this can lead to the notified bodies refusing or withdrawing the certificate. In principle, what the auditor checks is known (see Fig. 1):
- Auditors check whether the QM system with its specification documents covers all aspects of the standard, for example whether there is a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for internal audits that conforms to the standard.
- Auditors check whether the organization has complied with the requirements of its own QM system i.e. SOPs.
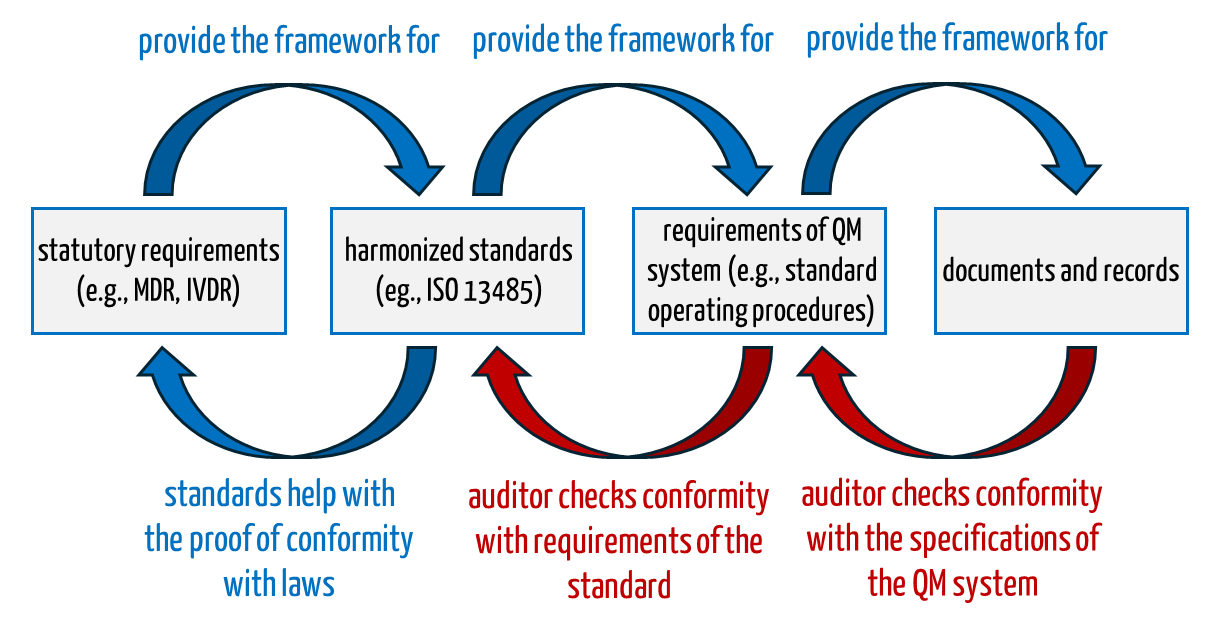
Fig. 1: Auditors check during the audit the conformity of the QM system with normative and legal requirements as well as the conformity with the company’s own QM system.
b) Special case of offsite audits
In a notice, the EU has regulated in more detail when and how notified bodies may carry out remote audits:
Calls for the possibility to take temporary extraordinary measures, including remote audits, related to notified body on-site audits under the medical devices Regulations have been made by industry as well as notified bodies.
The MDCG has published a Guidance on temporary extraordinary measures related to medical device Notified Body audits during COVID-19 quarantine orders and travel restrictions.
In it, it allows facilitations, e.g:
- Delayed on-site surveillance audits
- Replacement of audits with remote audits
- Offsite inspection / review of technical documentation
3. Support with audits
Do you still have questions, for example about setting up your QM system? Then take advantage of our free micro-consulting service.
The consultants at the Johner Institute not only support you in setting up QM systems, but also audit these systems and prepare you for audits (e.g., with mock audits and mock inspections).
Are you interested? Then contact us right away.
This seminar will give you the competence you need to act as an internal auditor.
