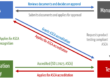
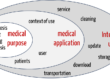
The IEC 61010 series of standards specifies safety requirements for electrical equipment used for measurement, control, regulation, and laboratory use. The general standard IEC 61010-1 and the particular standards of the IEC 61010-2 series describe the state of the art and thus serve IVD manufacturers as a means of demonstrating compliance with the general safety and performance requirements of Annex I of the IVD Regulation (IVDR).
1. The IEC 61010 series of standards
a. Scope
IEC 61010 is a series of standards that formulates safety requirements for electrical measuring, controlling, regulating, and laboratory equipment.
The term “laboratory” should not be understood as referring to a medical laboratory. For example, food laboratory devices also fall within the scope of the series of standards.
The series of standards is divided into Parts 1 and 2.
b. IEC 61010-1: The general standard
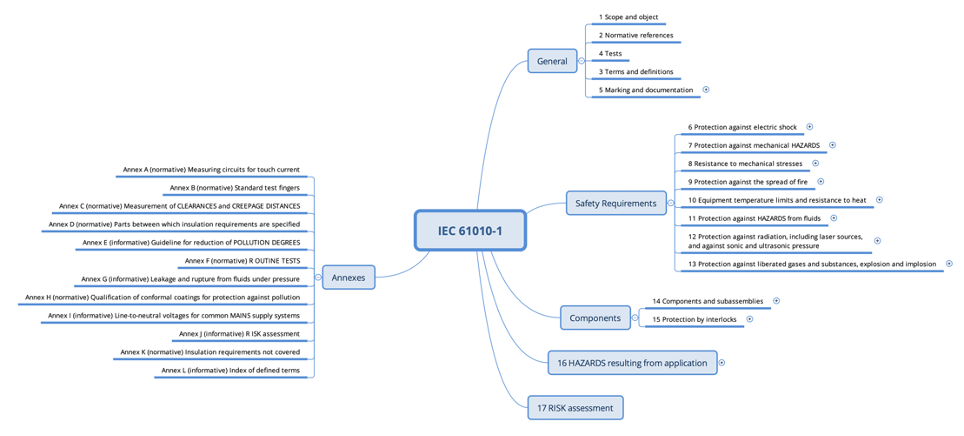
The general standard IEC 61010-1 specifies the basic general safety requirements that apply equally to all electrical measuring, control, regulation, and laboratory devices, regardless of their specific application.
Laboratory and IVD medical devices are process systems in which samples are prepared and processed in several steps for analysis or measurement. The samples are, for example, irradiated, heated, cooled, electrically activated, forwarded, stirred, or shaken.
Laboratory equipment poses a large number of hazards to people and the environment. Sections 6 to 13 of the standard, therefore, contain specific safety requirements for protecting users and the surrounding area against these hazards.
- Electrical hazards
- Mechanical hazards
- Hazards caused by escaping flames
- Thermal hazards
- Hazards caused by liquids and their pressure
- Hazards caused by gases
- Hazards caused by radiation
In accordance with the requirements of IVDR and ISO 14971, the standard follows the concept of integrated safety and specifies requirements at various levels:
- Limitation of hazardous energies
- Means of protection to control hazards
- Informational safety engineering (information)
Risks due to lack of performance, electromagnetic interference, or software defects are not covered. Although standalone software is powered by electricity, it does not fall within the scope of the series of standards.
c. IEC 61010-2-xx: The particular standards
The Part 2 standards IEC 61010-2-ff contain additional or modified requirements specifically tailored to certain equipment classes or applications. The objective of these Part 2 standards is to cover application-specific risks arising from certain technical aspects, such as heating or cooling.
- Part 2-010: Particular requirements for laboratory equipment for the heating of materials
- Part 2-081: Particular requirements for automatic and semi-automatic laboratory equipment for analysis and other purposes
- Part 2-101: Particular requirements for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) medical equipment
- Part 2-120: Particular safety requirements for machinery aspects of equipment
EN IEC 61010-2-101 is the harmonized standard for in vitro diagnostic (IVD) medical devices.
d. Interaction between standards from Part 1 and Part 2
The standards in Part 2 of the series supplement or modify the corresponding sections of the IEC 61010-1 standard. Therefore, they are structured in the same way (see Fig. 2).

For example, an IVD medical device within the scope of IEC 61010-2-101 must meet the requirements of both IEC 61010-1 and IEC 61010-2-101. The Part 2 standard overrides or supplements certain requirements of the Part 1 standard.
e. Delimitation of the scope of IEC 61010-1 and IEC 60601-1
Scope of IEC 61010
The scope of IEC 61010 covers the following electrically operated devices and their accessories:
- Devices that test, measure, display, or record physical quantities, including non-measuring devices such as signal generators
- Devices that control one or more output quantities to specific values
- Test equipment integrated into manufacturing processes and intended for the testing of manufactured equipment
- Equipment for measuring, indicating, monitoring, testing, or analyzing materials or for reprocessing materials, including in vitro diagnostic (IVD) equipment
Scope of IEC 60601-1
Medical devices that must be connected to the patient to fulfill their purpose, i.e., that have a so-called applied part, do not fall within the scope of IEC 61010. The safety and performance of such medical devices (ME Equipment/Systems) is covered by the IEC 60601-1 series of standards. IEC 61010-1, on the other hand, assumes that only (healthy) users come into contact with the device.
Examples
Examples of medical device applications and the leading safety standard are:
| Electrical medical device | Connection to the patient? | Standard |
| PCR test device | No | IEC 61010-1 |
| Respirator | Yes, tube set | IEC 60601-1 |
| Pipetting system for sample preparation | No | IEC 61010-1 |
| ECG machine | Yes, ECG electrodes | IEC 60601-1 |
| Device for external blood gas analysis | No | IEC 61010-1 |
| Blood glucose meter (self-testing) | Yes, lancet | IEC 60601-1, ISO 15197 |
| Blood glucose meter in the laboratory | No | IEC 61010-1 |
Special cases
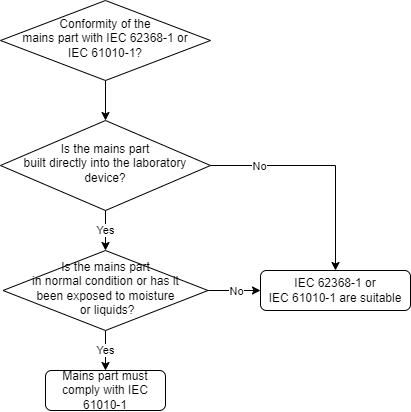
The distinction from medical electrical equipment is clear, but not always unambiguous for certain components. The mains part, for example, may fall under IEC 62368 (IT equipment) or IEC 61010-1 (laboratory equipment). If it is specifically designed for laboratory applications, IEC 61010-1 applies. If a standard power supply unit in accordance with IEC 62368 is used, it must be checked whether it meets the stricter requirements for moisture and liquids, for example.
2. IEC 61010-2-101: Particular requirements for IVD medical devices
a. Scope
IEC 61010-2-101 applies to devices intended for in vitro diagnostic (IVD), including IVD devices for self-testing, i.e., all in vitro diagnostic medical devices as defined in the IVDR Regulation. Self-testing refers to devices used by lay persons in a domestic environment.
The scope also includes computers or parts thereof that are part of the IVD medical device and have been explicitly designed to be used with these devices.
b. Requirements of IEC 61010-2-101
IEC 61010-2-101 is intended to be used in conjunction with the general standard (IEC 61010-1). It addresses the same physical hazards as the general standard and contains additional requirements regarding chemical and biological hazards.
The standard specifies the requirements in the following areas in more detail or as a supplement (status EN 61010-2-101:2024):
| Section | Supplements (selection) |
| 5 – Marking and documentation | Information on the type plate: – Symbols to be used – Labeling of connections – Instructions for installation and setup – Instructions for transport – Instructions for operation and disposal – Information on service life |
| 6 – Protection against electric shock | Additional test requirements |
| 7 – Protection against mechanical hazards | Non-obvious hazards such as: – Sharp edges – Moving masses – Falling over, jamming, crushing – Parts being thrown out Note: The requirements of IEC 61010-1 sufficiently reduce the risks associated with mechanical hazards. |
| 8 – Resistance to mechanical stresses | Further requirements for transport and storage |
| 9 – Protection against the spread of fire | No additional or changed requirements |
| 10 – Protection against excessive heat and cold | No additional or changed requirements |
| 11 – Protection against hazards from fluids and solid foreign objects | No additional or changed requirements |
| 12 – Protection against radiation, including laser sources, and against sonic and ultrasonic pressure | Protection against the effects of internally generated ultraviolet, ionizing, and microwave radiation, laser sources, sound and ultrasonic pressure, and electromagnetic radiation |
| 13 – Protection against liberated gases and substances, explosion and implosion | Additional requirements regarding biohazardous substances |
| 14 – Components and subassemblies | Additional requirements for overheating protection devices |
| 15 – Protection by interlocks | Reliability factors can be determined using functional safety methods |
| 16 – Hazards resulting from application | Note that risks relating to ergonomic aspects should be considered in accordance with IEC 62366 |
| 17 – Risk management | Requirement that risk management must be carried out in accordance with ISO 14971 |
IEC 61010-2-101 does not contain any performance requirements for IVD medical devices related to their intended purpose. The performance requirements are either contained in other standards, such as ISO 15197 for blood glucose meters, or must be specified by the manufacturer.
Unlike IEC 60601-1, the standard does not contain any requirements regarding software development.
c. Interaction with Part 2 standards
IVD medical devices with technical characteristics addressed in other Part 2 standards, such as centrifuges, must also comply with the relevant Part 2 standard.
For example, a machine analysis system that processes large sample volumes and contains fast-moving axes would have to comply with IEC 61010-2-101.
d. Interaction with risk management
General
The series of standards can be understood as a risk analysis. It addresses risks associated with physical, chemical, and biological hazards. For risks not addressed in the standard, the general standard IEC 61010-1 requires analyzing and controlling these risks, but does not specify the application of a particular risk management procedure.
Interaction with ISO 14971
In contrast, IEC 61010-2-101 explicitly requires in section 17 that the risk management procedure be carried out in accordance with the requirements of ISO 14971. The standard for ME equipment, IEC 60601-1, excludes activities for monitoring production and the post-production phases. This is not the case with IEC 61010-2-101. Manufacturers must therefore compile a complete risk file in accordance with ISO 14971 to demonstrate conformity.
Read more about the application of ISO 14971 here.
Interaction with further standards
The standard cites the application of functional safety methods in accordance with IEC 61508, IEC 62061, or ISO 13849 as further methods for risk analysis. In contrast to ISO 14971, these functional safety standards define standardized safety targets for specific safety functions. Manufacturers can then use industrial components such as safety switches, emergency stop controls, or light barriers that are already certified for a specific safety objective.
Manufacturers of IVD medical devices or systems that are also classified as machinery can benefit, in particular, from the functional safety methods to purchase already certified safety components. You can find an article on functional safety here. We recommend that manufacturers of small devices without machine characteristics apply ISO 14971.
The Johner Institute recommends creating a safety concept that describes the safety functions and their designs and calculations in every case.
3. EMC for IVD medical devices
a. Introduction
IEC 61010-2-101 does not contain any direct specifications for the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of laboratory or IVD medical devices, but refers to applying the IEC 61326-2-6 standard.
The IEC 61326 series of standards specifies EMC requirements for electrical measuring, control, regulation, and laboratory equipment and differentiates between different application areas. IEC 61326-1 is the general standard with general requirements, while specific parts such as -2-1 to -2-6 provide additional requirements for certain groups of equipment, such as portable equipment, precision measuring equipment, or medical test equipment.
IEC 61326-2-6 is specifically aimed at devices for in vitro diagnostics and ensures that they operate reliably and without interference in medical environments.
b. Requirements of IEC 61326-1
The title of the IEC 61326-1 standard is “Electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use – EMC requirements – Part 1: General requirements.”
The standard contains nine sections with the following contents:
| Section | Key aspects |
| 1 – Scope | Scope limited to electrical measuring, controlling, regulating, and laboratory equipment; IVD medical devices are included |
| 2 – Normative References | References to metrological standards |
| 3 – Terms, definitions and abbreviations | Applicable definitions from IEC Electropedia: http://www.electropedia.org/ |
| 4 – General | Note that devices and systems are resistant to electromagnetic interference and do not cause any disruptive emissions that could impair the function of other devices |
| 5 – EMC test plan | An EMC test plan must be drawn up before the tests begin. The EMC test plan contains aspects, such as test setup, configurations, operating modes, acceptance criteria, etc. |
| 6 – Immunity requirements | Tests to be performed and degrees of test severity depending on the electromagnetic environment |
| 7 – Emission requirements | The classification of the devices and the permissible limit values for interference emission in the intended environment |
| 8 – Test results and test report | Requirements for documenting test results in a test report |
| 9 – Instructions for use | The IFU must specify the electromagnetic environment for which the device is intended and the standard(s) that have been applied |
| Annex A | Requirements for the immunity test for portable test and measurement equipment powered by a battery or from the circuit under measurement |
| Annex B | Guidelines for the analysis and assessment of electromagnetic compatibility |
| Annex ZA | Normative references to international publications with their corresponding European publications |
c. Requirements of IEC 61326-2-6
In addition to the scope of IEC 61326-1, Part 2-6 specifies minimum requirements for immunity and emissions regarding electromagnetic compatibility for IVD medical devices, taking into account the special features and specific aspects of these electrical devices and their electromagnetic environment.
In version 4 of the standard from 2025, the scope of the standard changes in the title from “in vitro diagnostic medical equipment” to “in vitro diagnostic medical electrical equipment (IVD-MEE)”. This clarifies that only electrically powered IVD devices fall within the scope of the standard. The term MEE also makes it clear that the EMC requirements for laboratory equipment in the field of IVD are based on the stricter test conditions for medical devices that come into contact with patients.
Accordingly, the electromagnetic environments for IVD-MEE are divided into the two areas:
- Professional healthcare facility environment: an environment in which professional healthcare is provided
- Home healthcare environment: an environment with a more diverse electromagnetic environment that is less easy to characterize
The standard continues to adopt the concepts of “basic safety” and “essential performance” from IEC 60601-1, which are not included in the IEC 61010 series.
freedom from unacceptable risk to the operator directly caused by physical hazards when IVD MEDICAL EQUIPMENT is used under normal condition and single fault condition
performance of a clinical function, other than that related to BASIC SAFETY, where loss or degradation beyond the limits specified in the user documentation results in an unacceptable risk
The essential performance characteristics relate to the analytical performance of a device. Their deterioration can lead to an unacceptable risk. Section 4.101 of the 4th edition of the standard provides guidance on the step-by-step derivation of the essential performance characteristics. The risk analysis serves as proof that these steps have been carried out.
While the IEC 61010-1 series of standards focuses on basic safety, IEC 61326-2-6 also considers how electromagnetic interference affects analytical performance.
The aim of IEC 61326-2-6 is to demonstrate that basic safety (example: failure of a light barrier) or essential performance characteristics (example: incorrect measurement of a concentration) are not adversely affected by electromagnetic interference.
Further requirements are:
- Application of ISO 14971 for the derivation of acceptance criteria for the acceptability of risks
- Specification of degrees of test levels when testing susceptibility to interference for both electromagnetic environments
- Additional specifications for warnings in the instructions for use
d. Comparison with IEC 60601-1-2 for ME Equipment
IEC 60601-1-2 specifies requirements for the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) of medical devices (MD devices/systems) that are used directly on patients.
The IEC 60601-1-2 and IEC 61326-2-6 standards are comparable in terms of content and testing techniques: Both require risk management, the creation of an EMC test plan, and compliance with limits for interference emission and immunity testing.
The two standards define different levels of testing severity for the Professional Healthcare Facility Environment (PHE) and Home Healthcare Environment (HHE) application environments. With minor deviations, the same testing severity levels apply to IVD-MEE as to ME devices.
The following table illustrates this with an example:
| Test standard | Interference immunity test | ||
| IEC 61326-2-6 PHE | IEC 61326-2-6 HHE | IEC 60601-1-2 PHE | |
| ESD IEC 61000-4-2 | ± 4 kV contact ± 2 kV, ± 4 kV, ± 8 kV air | ± 8 kV contact ± 2 kV, ± 4 kV, ± 8 kV, ± 15 kV air | ± 8 kV contact ± 2 kV, ± 4 kV, ± 8 kV, ± 15 kV air |
| Electromagnetic field IEC 61000-4-3 | 3 V/m (80 MHz – 6 GHz) | 10 V/m (80 MHz – 1 GHz) 3 V/m (1 GHz – 6 GHz) | 3 V/m 80 MHz – 2,7 GHz (80 % AM at 1 kHz) |
e. FDA “EMC Guidance” with further requirements
While the FDA has only partially recognized the third version from 2021, it fully recognizes the fourth edition of the standard from 2025. Since 2010, the FDA has documented a tenfold increase in EMC-related device problems. In particular, interference from wireless communication and electromagnetic compatibility has increased dramatically, and the causes of this are difficult to analyze. Instead of reactive post-market problem solving, the fourth edition of the standard takes a preventive approach with risk-based management and increased testing levels to proactively ensure patient safety.
The FDA requires manufacturers to establish acceptance criteria that specifically relate to the functions and intended use of the respective IVD device. To this end, the essential performance characteristics should be clearly defined and the immunity tests aligned accordingly. A procedure for deriving these characteristics is described in section 4.101 of the 4th edition.
In addition, in its 2022 EMC guidance, the FDA recommends using the test severity levels of IEC 60601-1-2 – or, alternatively, an assessment of reasonably foreseeable electromagnetic phenomena in the intended environment of use, e.g., through literature studies or in-house measurements.
Manufacturers should read the EMC Guidance from the FDA dated June 2022 for guidance on applying EMC principles.
f. Overview of changes in the 4th edition of EMC 2025
IEC 61326-2-6:2025 not only introduces stricter test levels, but also a change in philosophy: from rigid table values to more risk management. The changes reflect the reality of modern electromagnetic environments, such as NFC smartphones, RFID access cards, more powerful MRI machines, and more electronics everywhere.
The most important changes at a glance
1. Massive tightening of immunity test levels
- Magnetic field: Tenfold increase from 3 to 30 A/m (only IVD with magnetically sensitive components)
- Electromagnetic fields: Standardization to 10 V/m + new AM modulation
- Burst/surge: Partial doubling of test voltages
- Fault tolerance: The correct functioning of protective measures to ensure basic safety is monitored during testing.
2. Increased focus on risk management approach
- Performance criteria: Performance criteria (A, B, C) completely removed – new: Essential performance characteristics and basic safety
- Variable test levels: Instead of fixed tables, variable test levels based on actual transmission power
- Country-specific: Certain frequencies may vary depending on the country.
- Magnetic fields: Four-level assessment for the need for testing in the near field (IEC 61000-4-39)
3. New: NFC, RFID & modern radio communication
- New Table 104: Tests for proximity magnetic fields
- Test frequencies: 30 kHz; 134.2 kHz; 13.56 MHz (NFC)
- Test level: Up to 65 A/m
- Acceptance: Communication interference is acceptable as long as essential performance characteristics and basic safety are maintained
4. Information in the user manual
- Documentation: Nine detailed documentation requirements (sections a to i)
- Essential performance characteristics: Disclosure of essential performance characteristics, in particular information on restoration
- Mobile phone distance: Formula d = 6/E √P no longer applies, replaced by a minimum distance rule of 30 cm
- Deviations: Deviations from test tables 101 to 104 must be documented.
Action required:
- Check the extent to which the product is affected by the changes
- Adapt the risk analysis with regard to new requirements
- Check magnetic field protection – particularly critical for interference-sensitive components
- Update instructions for use – new documentation requirements
- Update EMC test plan and repeat tests if necessary
- Define essential performance – critical in the absence of performance criteria
4. Conformity assessment
a. Tests that must be performed
The testing of IVD medical devices to verify basic safety is carried out in accordance with the requirements of IEC 61010-1 and IEC 61010-2-101 and other applicable Part 2 standards. In addition to the requirements, the standards also describe the tests to be carried out.
The tests should also include “single-fault conditions” in protective measures such as interrupting a protective earth conductor or blocking a fan. The test should also be carried out under normal and unfavorable operating conditions. This applies to aspects such as cable lengths, accessories, installation, power supply, and motor loads. Furthermore, possible application errors (easily foreseeable human error) should be simulated.
While the standards only cover basic safety, manufacturers must plan, carry out, and record the verification and validation of (analytical) performance themselves.
The following tests must be carried out to demonstrate conformity:
- Safety test according to IEC 61010-1 ff.
- EMC test according to IEC 61326-2-6 considering the IEC 60601-1-2 in POC environment
- Proof of analytical performance
- System tests and functional tests
- Formative and summative testing of usability
- Verification of the label and the operating instructions
b. Role of external laboratories
Conformity testing should be carried out in external, independent testing laboratories. External testing laboratories issue internationally recognized test reports, and manufacturers also benefit from the examiners’ experience. Notified bodies hardly ever recognize self-generated test reports (even if theoretically possible).
Software tests are not part of the type testing in the test laboratory. Certain parts of the device software are verified indirectly during EMC testing if they influence basic safety or essential performance.
c. Final test in production
The standards do not contain specifications for final production tests or intermediate tests during manufacture. The manufacturer must determine the necessity of such tests through a production risk analysis.
We recommend that at least the following tests be carried out as a final test:
- Measurement of the earth leakage current for class I
- Measurement of the protective conductor resistance for class I
- Measurement of the touch current
- Insulation tests on systems with extensive manual wiring
- Pressure and leak tests for liquids and gases
- Visual inspection of the means of protection
- Functional check of protective devices such as interlocks
- Functional tests
- Completeness of labels and warning notices
5. Conclusion and summary
The IEC 61010-1 series of standards, particularly IEC 61010-2-101, forms the safety basis for electrical equipment in vitro diagnostics (IVD).
While IEC 61010-1 covers the general requirements for basic safety, IEC 61010-2-101 specifies these requirements for the IVD sector, particularly with regard to patient protection, biological hazards, and typical use in laboratory environments.
Manufacturers must understand and implement both standards in conjunction with each other to meet regulatory requirements and ensure the safety and dependability of their devices in everyday medical use.
In addition, manufacturers should consider the EMC requirements and thus the IEC 61326 family of standards.
The IVD and IEC 61010 experts at the Johner Institute ensure that manufacturers bring their IVD medical devices to market in compliance with the law, safely, and with minimal effort. Among other things, they provide support in:
- Checking which standards are applicable
- Determining the relevant requirements from the standards
- Deriving the essential performance characteristics
- Creating an EMC test plan
- Reviewing and creating safety concepts
Get in touch right away here using the contact form
Change history:
- 2025-09-22: Addition to the amendments to the 4th edition of the EMC standard EN IEC 61326-2-6
- 2025-05-23: Article completely rewritten
- 2017-01-12: First version of article published